For users who have installed Adobe product, such as Photoshop or Lightroom, you can follow the steps to convert raw image to JPEG on mac. Convert Raw to JPEG on Mac Using Adobe Photoshop. Right click on raw image and open with Photoshop. Go to FileSave As. Choose Output as JPEG from the output menu. I can't seem to be able to download Canon RAW files, neither from an old S45 or from my newer Rebel XT. When I hook the camera to the mac, Iphoto comes up and downloads all files automatically, except the RAW files. When I try to use the Canon software, it will not detect the camera. Is there a simple way to download RAW files to a Mac?
Free Raw Files
iCloud Photos keeps your photos and videos up to date on your iPhone, iPad, iPod touch, and Mac. If your photo library includes images in RAW format, you can view and edit them on your Mac or iPad.
About RAW files on your Mac
The availability of RAW files on your Mac depends on a few conditions:
- If you have the Download Originals to this Mac option turned on in Photos (Photos > Preferences > iCloud > Download Originals to this Mac), then your RAW files are always present in Photos on your Mac.
- If you have the Optimize Mac Storage option turned on, then your RAW files are stored in iCloud Photos. The Photos app saves disk space on your Mac by displaying optimized JPEG versions of your RAW images. If you edit an optimized image on your Mac, Photos downloads the RAW file for that image.
- When Photos downloads a RAW image from iCloud Photos, it creates a new full-sized JPEG for optimal viewing on your Mac. It won't replace the RAW and embedded JPEG file already stored in iCloud. iOS devices will view the embedded JPEG.
- RAW files that you store outside the Photos app library (for example, in your Pictures folder) are always present on your Mac, but aren't stored in iCloud and won't stay up to date in the Photos app on your iPhone, iPad, or iPod touch.
About RAW files imported to iPad with the Camera Connection Kit
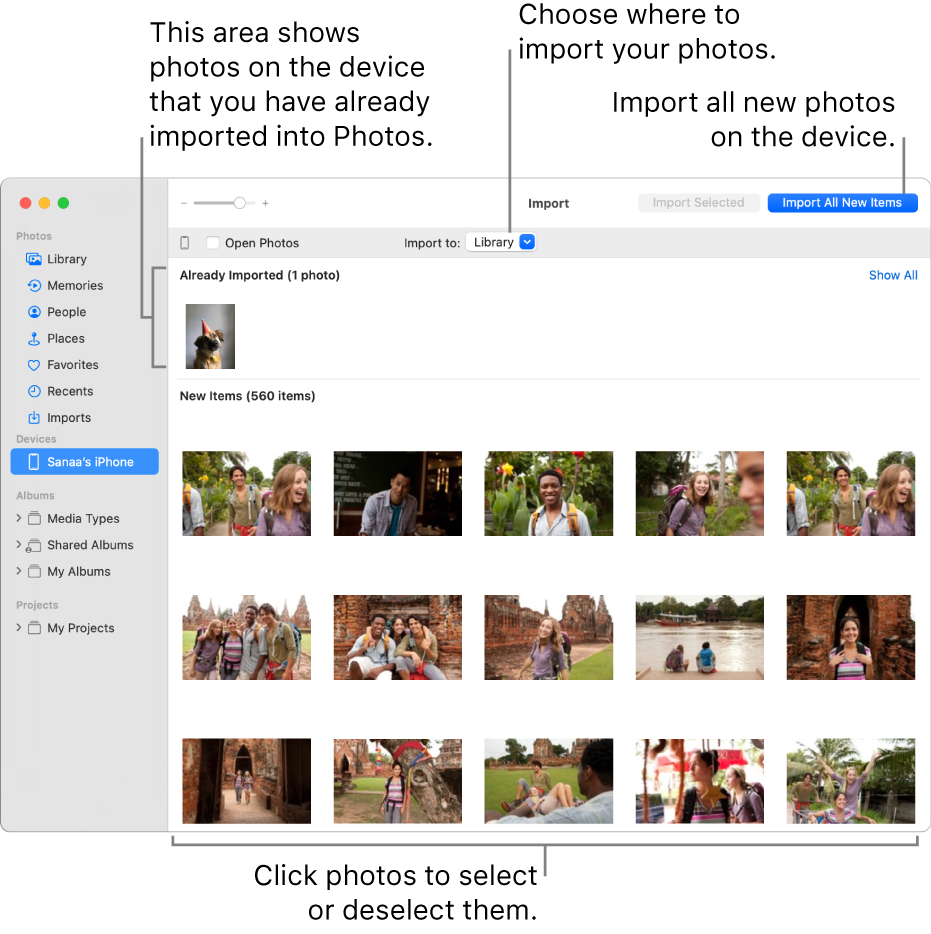
If you import RAW images to an iPad with the Camera Connection Kit, turn on Download Originals or edit the images on your Mac so that the files are available on your Mac in iCloud Photos.
Tutorial
Client URL, or cURL, is a library and command-line utility for transferring data between systems. It supports many protocols and tends to be installed by default on many Unix-like operating systems. Because of its general availability, it is a great choice for when you need to download a file to your local system, especially in a server environment.
In this tutorial, you’ll use the curl command to download a text file from a web server. You’ll view its contents, save it locally, and tell curl to follow redirects if files have moved.
Downloading files off of the Internet can be dangerous, so be sure you are downloading from reputable sources. In this tutorial you’ll download files from DigitalOcean, and you won’t be executing any files you download.
Step 1 — Fetching remote files
Out of the box, without any command-line arguments, the curl command will fetch a file and display its contents to the standard output.
Let’s give it a try by downloading the robots.txt file from Digitalocean.com:
You’ll see the file’s contents displayed on the screen:
Give curl a URL and it will fetch the resource and display its contents.

Saving Remote Files
Fetching a file and display its contents is all well and good, but what if you want to actually save the file to your system?

To save the remote file to your local system, with the same filename as the server you’re downloading from, add the --remote-name argument, or use the -O option:
Your file will download:
Instead of displaying the contents of the file, curl displays a text-based progress meter and saves the file to the same name as the remote file’s name. You can check on things with the cat command:
The file contains the same contents you saw previously:
Now let’s look at specifying a filename for the downloaded file.
Step 2 — Saving Remote Files with a Specific File Name
You may already have a local file with the same name as the file on the remote server.
To avoid overwriting your local file of the same name, use the -o or --output argument, followed by the name of the local file you’d like to save the contents to.
Execute the following command to download the remote robots.txt file to the locally named do-bots.txt file:
Once again you’ll see the progress bar:
Now use the cat command to display the contents of do-bots.txt to verify it’s the file you downloaded:
The contents are the same:
By default, curl doesn’t follow redirects, so when files move, you might not get what you expect. Let’s look at how to fix that.
Step 3 — Following Redirects
Thus far all of the examples have included fully qualified URLs that include the https:// protocol. If you happened to try to fetch the robots.txt file and only specified www.digitalocean.com, you would not see any output, because DigitalOcean redirects requests from http:// to https://:
You can verify this by using the -I flag, which displays the request headers rather than the contents of the file:
The output shows that the URL was redirected. The first line of the output tells you that it was moved, and the Location line tells you where:
You could use curl to make another request manually, or you can use the --location or -L argument which tells curl to redo the request to the new location whenever it encounters a redirect. Give it a try:
How To Read Raw Files
This time you see the output, as curl followed the redirect:
You can combine the -L argument with some of the aforementioned arguments to download the file to your local system:
Warning: Many resources online will ask you to use curl to download scripts and execute them. Before you run any scripts you have downloaded, it’s good practice to check their contents before making them executable and running them. Use the less command to review the code to ensure it’s something you want to run.
Conclusion
curl lets you quickly download files from a remote system. curl supports many different protocols and can also make more complex web requests, including interacting with remote APIs to send and receive data.
You can learn more by viewing the manual page for curl by running man curl.